What is MSG ?
definition
It is the monosodium salt of glutamic acid, which is one of the most abundant amino acids in nature. The bulk products sold on the market are usually in the form of monohydrate, with the chemical formula C5H8NaNO4·H2O.
What is MSG made of?
It can be seen from its chemical formula C5H8NaNO4.H2O that it is composed of MSG and water.
What is the use of MSG in food?
It is an umami substance that can enhance the meaty and salty taste of foods and make them more delicious.
It is commonly used in Chinese food, canned vegetables, fine baked products, soups and broths, sauces, meat and meat products, condiments and condiments, and food supplements.
How is MSG made?
It is produced through a natural process-fermentation, followed by a process of neutralization and crystallization.
Here are 4 authoritative resources that mention the manufacturing process , from Wikipedia, EFSA, China's major manufacturer, and Ajinomoto.
Let's take a look at them one by one.
1. WIKIPEDIA
Generally speaking, the industrial production of monosodium glutamate is now produced through the fermentation of starch and sugar, such as corn starch and tapioca starch, instead of extracting and crystallization from seaweed when Japanese scientists first made it in 1908.
2. EUROPEAN FOOD SAFETY AUTHORITY
There are two bacteria approved for L-glutamic acid fermentation, one is Corynebacterium glutamicum from strain 2256; the other is a new transgenic strain from Corynebacterium glutamicum (ie strain EA-12) .
In both processes, glutamic acid is produced by fed-batch fermentation using plant-derived carbon sources (sucrose), nitrogen sources, salt and vitamins.
3. LARGE CHINESE MANUFACTURER
Starting from glucose fermentation, Corynebacterium glutamicum is used to produce glutamic acid, which is then neutralized with sodium carbonate. The subsequent steps are decolorization, filtration, crystallization, centrifugation, drying and so on.
4. AJINOMOTO
Ajinomoto said that their brand MSG AJI-NO-MOTO® produced in Brazil is made through the fermentation of sugar cane syrup. Here is a detailed flow chart.

Specification
structure
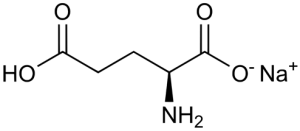
| Other names |
|
| appearance | A white, almost odorless crystalline granule or powder. |
| CAS number | 6106-04-03 (monohydrate) |
| Chemical formula | C5H8NaNO4.H2O |
| Molecular weight | 187.13 |
| Melting point | 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) |
| Solubility |
|
| Stablize | Stable under high temperature and light. After heating its 10% solution at 100ºC and pH 6.9 for 3 hours, about 0.6% of MSG will decompose. When heated to 120 ℃, it loses the combined crystal water. |
What is the purpose of MSG?
For more than one hundred years, it has been used as a flavor enhancer and umami seasoning in homes and restaurants all over the world. It has an umami taste, when added to food, it will enhance and enrich the salty (umami) and rich flavor of the food.
What are the common foods that use MSG?
The following are common MSG-containing foods and recommended dosages provided by Ajinomoto manufacturers .
| application | Use level |
| Meat products | ≥ 0.3% |
| broth | 15 – 25% |
| Soup | 6 – 8% |
| Seasoning: up to 10% salt | 50 – 70% |
| Seasoning: high salt content | 8 – 10% |
| Seasoning: instant noodles (ramen) | 10 – 17% |
| snack | 0.6 – 0.75% |
| Ketchup | 0.6 – 1.0% |
| mustard | 0.6 – 1.0% |
| Salad dressing | 0.4 – 0.6% |
| Vegetable preserves | 0.2 – 0.3% |
| Fish by-products | ≥ 0.3% |
| frozen food | |
| Biscuit | |
| Pasta dough |
Why do people worry about Chinese food?
CHINESE RESTAURANT SYNDROME
People usually associate MSG with Chinese food. Some people may experience chest pain, headache, skin flushing, sweating and other symptoms after eating in Chinese restaurants.
This experience is called "Chinese Restaurant Syndrome" which may be caused by MSG and was first reported in 1968.
Because of this problem, some people order Chinese food without MSG, and some even ask, "Does every Chinese restaurant use MSG?"
IS MSG ONLY ADDED TO CHINESE FOOD?
However, MSG is not only used in Chinese food. It is also commonly used in other Asian countries, such as Japan, where MSG was first discovered; in India, Pakistan, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia and other countries, you can easily find it as a flavor enhancer on the labels of many processed foods. The supermarket has its name or E621/621.
Although the safety has been approved by the FDA, it is well known that flavor enhancers can deceive our taste buds and send wrong signals to the brain, which makes it difficult for us to tell whether this dish is really good or not, and some people may even use it addictively.
So if you are worried about MSG in food, please go to a regular restaurant.
Is MSG safe?
Yes, safety has been approved as a food additive by FDA ( U.S. Food and Drug Administration ) and EFSA ( European Food Safety Agency ) .
Food and Drug Administration
The FDA considers the addition of MSG to food to be "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS). It is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. The FDA lists it together with amino acids in the "special dietary nutritional additives" list, and claims that it is a direct food additive that can be safely used as a nutrient added to food.
European Food Safety Agency
According to Annex II of Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on Food Additives, sodium glutamate (E 621) is authorized as a food additive by the European Union (EU) and is classified as "additives other than coloring and sweeteners".
2017 REASSESSMENT
Safety
No adverse reactions have been observed in studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, neurotoxicity, reproduction and developmental toxicity.
Name
In June 2017, EFSA derived a set of acceptable daily intake (ADI), which is 30 mg/kg body weight per day, expressed as glutamate.
side effect
EFSA also pointed to ADI related to MSG symptom complex (> 42.9 mg/kg), headache (85.8 mg/kg), increased blood pressure (150 mg/kg), and increased insulin (> 143 mg/kg).
REQUEST TECHNICAL DATA
EFSA is now calling for the provision of technical data so that MSG and other glutamate can be re-evaluated from April 2019 .
Include:
- Use level
- Functional and technical requirements
- Natural levels of free glutamate-glutamate in food
- Food ingredients rich in free glutamate and glutamate
- The lowest achievable limit of toxic elemental impurities
APPROVED USE
The approved application is classified as Group I of 67 food categories, and the highest level is "10 g/kg, alone or in combination, expressed as glutamic acid."
The following foods may contain it
- Dairy products and the like
- Fat and oil and fat and oil emulsion
- Edible ice cubes
- fruits and vegetables
- Candy
- Cereals and cereal products
- Baking supplies
- Meat
- Fish and fishery products
- Eggs and egg products
- Sugar, syrup, honey and tabletop sweeteners
- Salt, spices, soups, sauces, salads and protein products
- Foods used for specific nutritional purposes as defined in Directive 2009/39/EC
- drinks
British Food Standards Agency
Categorized in other.
Australia New Zealand Food Standard
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand, with the code 621. (10
Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives
Function category: Food additives: flavor enhancer (11
ADI: Since 1987, there has been no restriction on the use of MSG as a food additive and the acceptable daily intake setting is "unspecified". (12
What are the possible side effects?
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is a well-known and controversial ingredient. Consumers generally question whether MSG is harmful to our health and what side effects it has. Although the FDA and EFSA have recognized its safety for many years, it has often received public safety concerns.
- Why does MSG cause controversy?
- metabolism
- Allergies: headache, nausea, numbness, flushing, etc.
- Effects on the brain
- Does it cause cancer?
- Is it poisonous?
- Does it raise blood pressure?
- Will it cause obesity?
- Does it cause asthma?
- Will it hurt the liver?
- May damage the kidneys
- May cause type 2 diabetes
Why does MSG cause controversy?
For some people, its use is still controversial because people who are intolerant to it have many health problems. Common risks include headache, brain damage, neurotoxins, blood pressure, Chinese restaurant syndrome, etc.
Some consumers try to avoid it and turn to its alternatives because they think MSG is harmful to health. We understand that consumers care about the ingredients in the food we eat .
Let's start with metabolism and then discuss its possible side effects.
What is the metabolism in our body?
ABSORB
MSG is absorbed in the intestines and is metabolized in large amounts in the intestinal wall of our body.
METABOLISM
According to EFSA, MSG can be metabolized by the liver, brain and muscles.
- In the liver, it produces glucose, lactate glutamine and other amino acids.
- In muscle tissue, it is converted to alanine and glutamine.
- In the brain, it is metabolized to aspartic acid through transamination.
What is an allergy?
As the FDA said, some people are very sensitive to MSG. Symptoms of allergy may be as follows:
- Headache
- Atopic dermatitis
- Some sensitive people who consume 3 grams or more of MSG without food may experience nausea, numbness, flushing, tingling, palpitations, and lethargy.
What is the effect on the brain?
It is considered an excitotoxin because it damages the brain.
But a study published in 2018 by the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine found that MSG does not increase the concentration of glutamate in the brain.
Does it cause cancer?
There are no reports of a link between MSG and cancer.
Is MSG poisonous?
GENOTOXIN
A study published in Food Chem Toxicology in 2016 showed that MSG can cause DNA damage to isolated human lymphocytes after 1 hour in vitro exposure, and is genetically toxic to human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro.
NEUROTOXIN
A study published in 2018 showed that there is no evidence in the study that dietary MSG can cause neurotoxicity.
Does it raise blood pressure?
A finding reported by the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention in 2011 showed that MSG intake was associated with a significant increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, especially in women.
In addition, another study published by the University of British Columbia in 2015 found that repeated oral administration of MSG can cause high blood pressure, accompanied by nausea and headache.
Will it cause obesity?
In 2011 , published in the "American Journal of Clinical Nutrition," the study found that healthy adults eat Chinese MSG and development is closely related to being overweight.
However, the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention conducted more than 5 years of research on 1282 Chinese men and women and showed that MSG has nothing to do with obesity.
Similarly, another study published in " Nutrition and Metabolism" in 2012 showed that Thai people's intake of more MSG is associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome and overweight.
However, a study published in the journal " Public Health Nutrition" had the opposite result on Vietnamese adults.
Does it cause asthma?
An early study in an Australian hospital in 1987 found that when the MSG dose was increased from 0.5 g to 5.0 g within 12 hours, 13 of 32 patients (with asthma) developed asthma.
However, a study published in 2012 used 1 g, 5 g, and 25 mg/kg MSG doses in 24 adults to conclude that there is no evidence to support the avoidance of MSG in adults with chronic asthma, but the author also stated that the data are limited.
Will it hurt the liver?
A 2011 study in rats showed that MSG changed the dilation of the central vein, which is not good for the liver.
May damage the kidneys
A study published in 2015 found that MSG may be harmful to the kidneys.
May cause type 2 diabetes
In a 2019 study, MSG caused type 2 diabetes in animals.
Is it safe for pregnant women and breastfeeding?
Generally speaking, it is safe, but it is best to consult your doctor.
A rat study published in 2018 stated that “MSG may inhibit female reproductive function by impairing the function of the ovaries and uterus.
15 Frequently Asked Questions
Is it natural?
Yes, this is a naturally occurring source in many foods such as tomatoes and cheese.
Ajinomoto also said that glutamic acid is naturally present in meat, fish, milk and many vegetables.
According to FDA information, certain ingredients such as hydrolyzed vegetable protein , autolyzed yeast , hydrolyzed yeast, yeast extract, soybean extract, and protein isolate also naturally contain MSG.
Is it a vegetarian?
Yes, it is vegan because the raw material glutamic acid comes from the fermentation and manufacturing process and does not use animal substances or products derived from animals. As a food ingredient, it is considered vegetarian and vegetarians can consume it in their diet.
Is it halal?
Yes, it is halal food, which meets the habits and needs of Muslims. We can find several Chinese manufacturers that have obtained MUI halal certification.
Is it kosher?
Yes, this is kosher. E621 meets all "kashruth" requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it gluten-free?
What is the relationship between glutamate and gluten is a frequently asked question. But in fact there is no correlation between them.
Yes, it is gluten-free or gluten-free, meets the following conditions listed by the FDA, and does not contain wheat, rye, barley or hybrids of these grains from the raw materials and manufacturing process .
What is the taste of MSG?
This flavor is different from the existing four flavors (sweet, sour, bitter, and salty), and is called umami. The fifth flavor is meat or salty in English and "umami" in Chinese.
Which foods are high in MSG?
Cheese, ripe tomatoes, dried mushrooms, fermented fish sauce and fermented soy sauce contain high levels of free glutamic acid.
Yeast extract, soy sauce, and protein hydrolysate may also be rich in free glutamate and glutamate.
What are the benefits of MSG in food?
1. IMPROVED TASTE
MSG can enhance the flavor and mouthfeel characteristics. A small amount of MSG is added before, during or after cooking to make food taste better.
2. CONTRIBUTE TO LOW-SALT DIET
Salt (sodium chloride) is an ideal material in food, because it helps increase the salty taste, but in our diet we should control the amount of salt added to food, because too much sodium intake will increase the risk of high blood pressure and stroke And the risk of cardiovascular disease.
MSG contains about 12% sodium, while table salt NaCl contains about 39%. MSG gives food "umami" and salty taste.
Therefore, the use of monosodium glutamate and salt instead of part of the salt can reduce the sodium content of processed foods.
What is glutamate?
The salts of glutamate, including monosodium glutamate, and the ionic form of glutamate, are called glutamate.
It is the free form of glutamic acid, which can provide "umami" taste to food and has the effect of enhancing flavor, rather than combining with other amino acids as a part of protein.
Other glutamate salts such as monopotassium glutamate (E622), calcium glutamate (E623), monoammonium glutamate (E624) and magnesium glutamate (E625) can also be used as flavor enhancers in foods.
What is the role of glutamate?
Glutamate is a neurotransmitter in a healthy brain. It has an excitatory effect on nerve cells, and it can stimulate cell death in a process now called "excitotoxicity". Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system of mammals.
How to cook with MSG?
It is thermally stable and suitable for use before, during and after the cooking process:

The dosage, method and recommended amount of MSG for different cooking purposes are as follows

What is a substitute for MSG?
Alternatives such as I+G (made from disodium guanylate and disodium inosinate) and hydrolyzed vegetable protein.
Is yeast extract the same as MSG?
They are different. Yeast extract is another flavor enhancer, and it may contain MSG.
Does McDonald's food contain MSG?
McDonald’s response : “ MSG is a flavor enhancer widely used in the food industry and can be found in many foods you buy from your local grocery store. The use of MSG has been authorized by the food safety authority and is in our minority In products, such as wheat chicken, spicy wheat chicken, big chicken spicy and McArabia Chicken, we found traces of it as a sub-ingredient."
But in an earlier response from McDonald's Canada in 2012 , it stated that MSG is not used in any of its products because it may cause reactions in individuals who are sensitive to MSG due to its glutamate content. Use other flavor enhancers, such as hydrolyzed vegetable protein and hydrolyzed vegetable protein.
How to avoid MSG in food?
A 2018 article in the Washington Post stated that although MSG has been approved for decades, about 40% of Americans still try to avoid MSG.
So let's get into the topic, how to avoid it? Choosing MSG-free foods is well known.
Here are the 4 steps:
Step 1: Choose food ingredients that do not contain MSG
For this step, I think that although we know that several food ingredients contain MSG, as mentioned in this article, there may still be many foods that we don’t know whether they contain MSG.
Step 2: Choose seasonings without MSG
I think this step will be easier to do because you can ask the restaurant staff or check the seasoning label.
Step 3: Read food labels
Generally, MSG needs to list its specific name (ie MSG) or E number or code number (ie 621 or E621) and its functional category (flavor enhancer) in the ingredient list of the food label.
The FDA requires that the added MSG be listed on the food label so that you can easily identify it.
Step 4: Be careful
Many products and restaurants claim that "no MSG is added" means that they do not add MSG during food processing, but remember that there may be naturally occurring glutamate in food.
in conclusion
Now you may have a good understanding of the production of food additives-MSG E621 ; uses; approved safety, possible side effects and answers to some common questions, such as vegan, gluten-free, synthetic or natural.














